Teams are groups of people working together for a common goal. The best teams can be multi-functional and have members with different beliefs and cultures. Great teams are built by developing and encouraging each member. The key to success in any business is a cohesive and well-organized team.
Collaboration to reach a common goal
A key skill for any workplace is the ability to work together in order to reach a common goal. Everyone on the team needs to contribute their skills, knowledge, and experience in order to be a team player. Without teamwork, it is nearly impossible to achieve the common goal. There are many methods to encourage effective teamwork.
A way to increase teamwork is to look at the bigger picture. When people come from different backgrounds and have different approaches, it can be difficult for them to agree on a common goal. To understand what everyone is focused on, it's important to have an open and honest dialogue. This will allow everyone in the group to achieve the same goal and help them to be more successful.

Five stages of team development
Each member of the team has learned how to collaborate with each other and developed trust and respect. As they become more comfortable and more proficient in their work, they will be more efficient and productive. The leader at this stage is usually only there to keep an eye on the team's progress and not get involved in the details.
Leaders should work to build long-lasting relationships with their team and celebrate the project's success. The team may be asked to assume additional responsibilities during this stage, such as overseeing project completion.
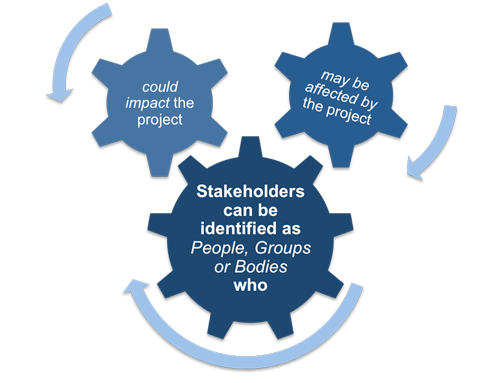
What makes a great team member?
A great team member has flexibility, willingness to work with other people, and the ability to be accountable. In addition, the ideal team member has a learning mindset and is never afraid to challenge their assumptions and opinions. He or she is willing to admit when they are wrong. He or she must also be open to sharing the spotlight with others and being a role model for younger members of the team.
A team member who is effective listens to their colleagues and communicates clearly without interrupting others. This is essential for teamwork success as it fosters honest and open communication. This allows team members to share their problems and ideas freely.
Understanding your team members
Understanding each member's preferences is key to improving team performance. This is possible with the DiSC assessment. This allows you to assess each team member's motivations, stressors, default behaviors and other motivators. It will also help you to better communicate with other team members and create positive working relationships.
Collaboration can only be achieved when everyone is understood. Knowing your team members is key to fostering a cooperative work environment. They will be able support one another better and can work together toward a common goal. To illustrate, a team that knows each member's strengths and weaknesses will be more successful in resolving conflicts. This will make collaboration easier and more productive.
FAQ
What are management principles?
Management concepts are the principles and practices used by managers to manage people, resources. These include topics such as human resource policies and job descriptions, performance assessments, training programs and employee motivation.
What are some common management mistakes?
Managers can make their jobs more difficult than necessary.
They may not be able to delegate enough responsibility to staff or provide adequate support.
In addition, many managers lack the communication skills required to motivate and lead their teams.
Managers can set unrealistic expectations for their employees.
Managers may choose to solve every problem all by themselves, instead of delegating to others.
How do you manage employees effectively?
Effectively managing employees means making sure they are productive and happy.
This also involves setting clear expectations and monitoring their performance.
Managers need to establish clear goals for their team and for themselves.
They need to communicate clearly and openly with staff members. They must communicate clearly with staff members.
They should also keep records of all activities within their team. These include:
-
What was achieved?
-
How much work was done?
-
Who did it?
-
What was the moment it was completed?
-
Why was it done?
This information can help you monitor your performance and to evaluate your results.
Statistics
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement a Quality Management Plan?
QMP (Quality Management Plan) is a system to improve products and services by implementing continuous improvement. It is about how to continually measure, analyze, control, improve, and maintain customer satisfaction.
QMP is a method that ensures good business performance. The QMP aims to improve the process of production, service delivery, and customer relationship. QMPs should cover all three dimensions - Products, Processes, and Services. The QMP that only addresses one aspect of the process is called a Process QMP. When the QMP focuses on a Product/Service, it is known as a "Product" QMP. QMP stands for Customer Relationships.
Scope is the most important element in implementing a QMP. Strategy is the second. These are the following:
Scope: This is the scope of the QMP and its duration. This will be used to define activities that are performed in the first six months of a QMP.
Strategy: This describes the steps taken towards achieving the goals set forth in the scope.
A typical QMP comprises five phases: Planning and Design, Development, Construction, Implementation, Maintenance. Here are the details for each phase.
Planning: This stage identifies and prioritizes the QMP's objectives. All stakeholders involved in the project are consulted to understand their requirements and expectations. The next step is to create the strategy for achieving those objectives.
Design: The design stage involves the development of vision, mission strategies, tactics, and strategies that will allow for successful implementation. These strategies are put into action by developing detailed plans and procedures.
Development: Here the development team works toward building the necessary resources and capabilities to support the successful implementation.
Implementation involves the actual implementation using the planned strategies.
Maintenance: The maintenance of the QMP is an ongoing task.
Additional items must be included in QMP.
Stakeholder involvement is important for the QMP's success. They are required to actively participate in the planning, design and development of the QMP, as well as the implementation and maintenance phases.
Initiation of a Project: A clear understanding and application of the problem statement is crucial for initiating a project. In other words, the initiator needs to know why they want to do something and what they expect from the outcome.
Time Frame: The time frame of the QMP is very critical. You can use a simplified version if you are only going to be using the QMP for short periods. You may need to upgrade if you plan on implementing the QMP for a long time.
Cost Estimation: Another important component of the QMP is cost estimation. You cannot plan without knowing how much money you will spend. It is therefore important to calculate the cost before you start the QMP.
QMPs are not just a written document. They should be a living document. It changes with the company. So, it should be reviewed periodically to make sure that it still meets the needs of the organization.